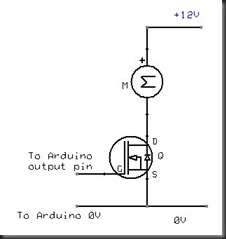
Podrán ver como hacer que se puedan controlar 8 relays desde visual Basic 2010, tan solo con un solo botón podrás activar y desactivar. También podrán observar como los indicadores cambiaran de color verde a rojo cuando el relay este activado, Podrán comparar con la publicación anterior y podrán notar los cambios realizados en el Sketch de arduino y también en Visual Basic.
No solo podrán controlar relays, pueden apilarlo en diferentes proyectos como prender motores, lámparas, entre otras cosas. Espero les guste.

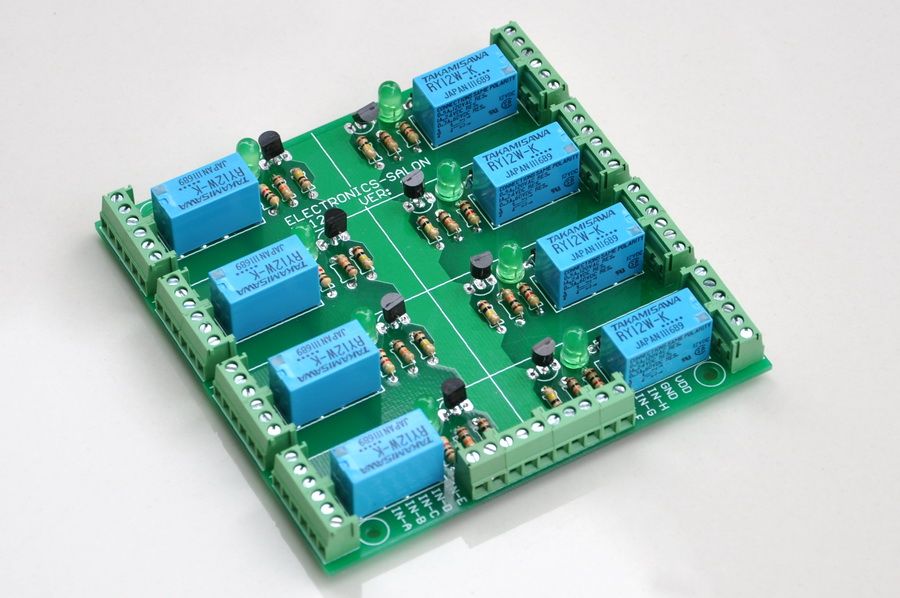
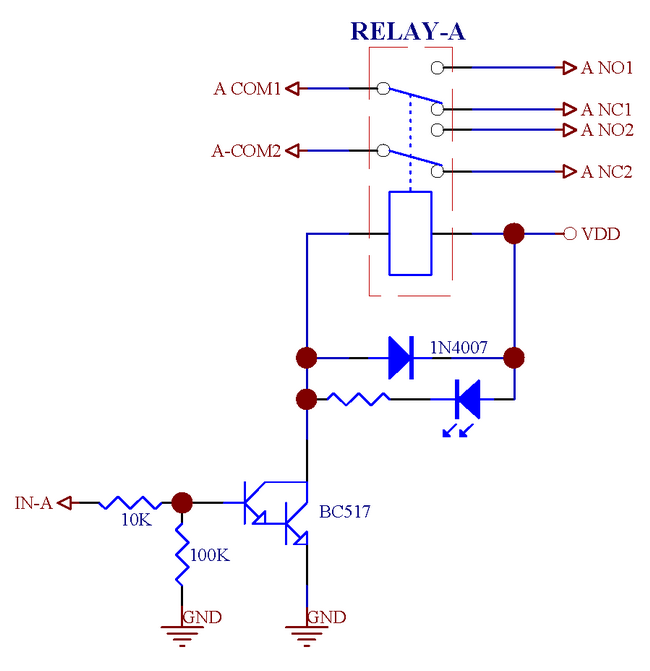
Podran utilisar diferentes paneles de relays :
 Aquí les dejo el Sketch de Arduino
Aquí les dejo el Sketch de Arduino
//apcexpert.blogspot.com
//Con este programa controlaras 8 relays con pulsar un boton para actibar y
//al pursarlo nuevamente se desactiva.
char inData[20]; // Allocate some space for the string
char inChar=-1; // Where to store the character read
byte index = 0; // Index into array; where to store the character
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
pinMode(12, OUTPUT);
pinMode(11, OUTPUT);
pinMode(10, OUTPUT);
pinMode(9, OUTPUT);
pinMode(8, OUTPUT);
pinMode(7, OUTPUT);
pinMode(6, OUTPUT);
}
char PinOut(char* This) {
while (Serial.available() > 0) // Don't read unless
// there you know there is data
{
if(index < 19) // One less than the size of the array
{
inChar = Serial.read(); // Read a character
inData[index] = inChar; // Store it
index++; // Increment where to write next
inData[index] = '\0'; // Null terminate the string
}
}
if (strcmp(inData,This) == 0) {
for (int i=0;i<19;i++) {
inData[i]=0;
}
index=0;
return(0);
}
else {
return(1);
}
}
void loop()
{
if (PinOut("13 on")==0) { digitalWrite(13, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("13 off")==0) {digitalWrite(13, LOW);}
if (PinOut("12 on")==0) { digitalWrite(12, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("12 off")==0) {digitalWrite(12, LOW);}
if (PinOut("11 on")==0) { digitalWrite(11, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("11 off")==0) {digitalWrite(11, LOW);}
if (PinOut("10 on")==0) { digitalWrite(10, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("10 off")==0) {digitalWrite(10, LOW);}
if (PinOut("9 on")==0) { digitalWrite(9, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("9 off")==0) {digitalWrite(9, LOW);}
if (PinOut("8 on")==0) { digitalWrite(8, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("8 off")==0) {digitalWrite(8, LOW);}
if (PinOut("7 on")==0) { digitalWrite(7, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("7 off")==0) {digitalWrite(7, LOW);}
if (PinOut("6 on")==0) { digitalWrite(6, HIGH);}
if (PinOut("6 off")==0) {digitalWrite(6, LOW);}
}
Visual Basic 2010
Imports System.IO
Imports System.IO.Ports
Imports System.Threading
Public Class Form1
' Shared _continue As Boolean
' Shared _serialPort As SerialPort
Dim pinout13 As Boolean = True
Dim pinout12 As Boolean = True
Dim pin11 As Boolean = True
Dim pinout10 As Boolean = True
Dim pinout9 As Boolean = True
Dim pinout8 As Boolean = True
Dim pinout7 As Boolean = True
Dim pinout6 As Boolean = True
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
SerialPort1.Close()
SerialPort1.PortName = "com4" 'Cambiar el numero de Puerto "COM"
SerialPort1.BaudRate = 9600
SerialPort1.DataBits = 8
SerialPort1.Parity = Parity.None
SerialPort1.StopBits = StopBits.One
SerialPort1.Handshake = Handshake.None
SerialPort1.Encoding = System.Text.Encoding.Default
End Sub
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pinout13 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("13 on")
RectangleShape1.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("13 off")
RectangleShape1.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pinout13 = Not (pinout13)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pinout12 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("12 on")
RectangleShape2.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("12 off")
RectangleShape2.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pinout12 = Not (pinout12)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub RectangleShape1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles RectangleShape1.Click, RectangleShape8.Click
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pin11 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("11 on")
RectangleShape3.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("11 off")
RectangleShape3.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pin11 = Not (pin11)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub Button4_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button4.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pinout10 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("10 on")
RectangleShape4.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("10 off")
RectangleShape4.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pinout10 = Not (pinout10)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub RectangleShape3_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles RectangleShape3.Click, RectangleShape6.Click
End Sub
Private Sub RectangleShape4_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles RectangleShape4.Click, RectangleShape5.Click
End Sub
Private Sub RectangleShape2_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles RectangleShape2.Click, RectangleShape7.Click
End Sub
Private Sub Button8_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button8.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pinout6 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("6 on")
RectangleShape8.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("6 off")
RectangleShape8.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pinout6 = Not (pinout6)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub Button5_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button5.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pinout9 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("9 on")
RectangleShape5.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("9 off")
RectangleShape5.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pinout9 = Not (pinout9)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub Button6_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button6.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pinout8 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("8 on")
RectangleShape6.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("8 off")
RectangleShape6.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pinout8 = Not (pinout8)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
Private Sub Button7_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button7.Click
SerialPort1.Open()
If pinout7 = True Then
SerialPort1.Write("7 on")
RectangleShape7.BackColor = Color.Red
Else
SerialPort1.Write("7 off")
RectangleShape7.BackColor = Color.Lime
End If
pinout7 = Not (pinout7)
SerialPort1.Close()
End Sub
End Class
Hasta la proxima.